Day trading, the thrilling pursuit of short-term stock market profits, requires a keen understanding of market dynamics and a carefully crafted strategy. This guide delves into the world of top stocks for day trading, exploring the factors that contribute to their selection, the inherent risks involved, and the techniques employed by successful traders. We’ll navigate the complexities of technical and fundamental analysis, charting techniques, and risk management strategies, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently approach this dynamic market.
From identifying potential opportunities using technical indicators and fundamental analysis to developing a personalized trading strategy and managing risk effectively, we will cover all the essential aspects. We will also explore the regulatory landscape, the use of options in day trading, and the importance of emotional control in this high-pressure environment. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a solid foundation for those seeking to navigate the exciting, yet challenging, world of day trading.
Understanding Day Trading and Top Stocks
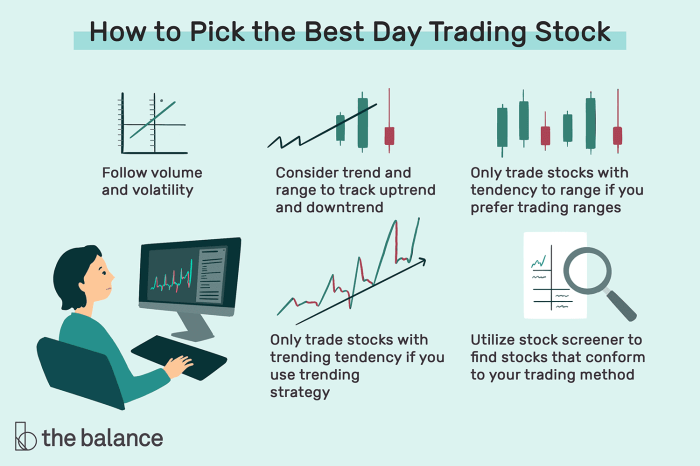
Day trading, the practice of buying and selling securities within the same trading day, presents both significant opportunities and substantial risks. Success hinges on understanding the characteristics of suitable stocks and employing effective risk management strategies. This section delves into the key aspects of selecting and trading stocks for day trading.
Characteristics of Stocks Suitable for Day Trading
Stocks ideal for day trading generally exhibit high liquidity, meaning they are frequently traded, allowing for easy entry and exit. High volume is another key characteristic; a high volume of shares traded indicates greater price volatility, offering more opportunities for profit. Furthermore, stocks with relatively narrow price ranges, allowing for precise entry and exit points, are generally preferred.
Finally, stocks that react strongly to news events or market trends are often targeted, as their price movements can be more easily predicted (though this prediction is never guaranteed).
Factors Influencing the Selection of Top Day Trading Stocks
Several factors influence the selection of stocks for day trading. Volatility, as previously mentioned, is crucial. Stocks with high beta (a measure of a stock’s price volatility relative to the overall market) often offer greater potential returns but also carry significantly higher risk. Price action analysis, which involves studying historical price charts to identify patterns and trends, plays a major role.
Technical indicators, such as moving averages and relative strength index (RSI), provide additional signals to aid in decision-making. Fundamental analysis, while less common in day trading, can also inform decisions by providing insights into a company’s financial health and future prospects. Finally, market sentiment, gauged through news headlines, social media, and overall market trends, can significantly influence a stock’s price.
Risks Associated with Day Trading and Risk Mitigation Strategies
Day trading carries inherent risks. The most significant is the potential for substantial financial losses. Rapid price fluctuations can lead to losses exceeding initial investments if proper risk management is not in place. Overtrading, driven by emotional decisions rather than a well-defined strategy, is another major risk factor. Lack of sufficient knowledge and experience can also lead to poor decision-making and consequent losses.
Information overload, leading to analysis paralysis or impulsive actions, is another risk.To mitigate these risks, several strategies are crucial. Utilizing stop-loss orders to automatically sell a stock when it reaches a predetermined price limit helps limit potential losses. Diversifying investments across multiple stocks reduces exposure to the risk of a single stock’s poor performance. Developing a well-defined trading plan, including entry and exit strategies, helps maintain discipline and reduces emotional decision-making.
Thorough research and continuous learning are essential to enhance trading skills and knowledge. Finally, maintaining a realistic expectation of returns and avoiding overtrading are crucial for long-term success.
Stock Screening Criteria for Day Trading
| Criterion | Description | Example | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Daily Volume | The average number of shares traded daily. | >1 million shares | High volume ensures liquidity. |
| Volatility (Beta) | A measure of price volatility relative to the market. | Beta > 1.5 | Higher volatility offers more trading opportunities but increases risk. |
| Price Range | The difference between the high and low prices. | Narrow range, < $5 | A narrow range allows for precise entry and exit points. |
| Liquidity | Ease of buying and selling shares. | High bid-ask spread | Essential for quick entry and exit. |
Identifying Potential Top Stocks
Pinpointing lucrative day trading opportunities requires a multifaceted approach, skillfully blending technical analysis with a nuanced understanding of fundamental factors. Success hinges on rapidly identifying stocks poised for significant short-term price movements, demanding a keen eye for market trends and a disciplined trading strategy. This section delves into the key tools and techniques employed by successful day traders to identify these potential top performers.
Technical Indicators for Day Trading Opportunities
Technical analysis utilizes past market data to predict future price movements. Several indicators prove particularly useful for identifying potential day trading opportunities. Relative Strength Index (RSI), for instance, measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions. An RSI above 70 often suggests a stock is overbought and potentially due for a correction, while a reading below 30 may indicate an oversold condition, potentially signaling a bounce.
Moving averages, such as the 50-day and 200-day simple moving averages (SMA), help identify trends. A bullish crossover occurs when a shorter-term moving average (e.g., 50-day SMA) crosses above a longer-term moving average (e.g., 200-day SMA), suggesting a potential upward trend. Conversely, a bearish crossover signals a potential downward trend. Volume analysis provides insights into the strength of price movements.
High volume accompanying a price increase confirms the strength of the uptrend, while high volume during a price decline indicates a strong downtrend. Bollinger Bands, which plot standard deviations around a moving average, can help identify potential reversals. Prices bouncing off the lower band might suggest a buying opportunity, while a break above the upper band could signal further upward momentum.
Fundamental Analysis in Short-Term Stock Selection
While primarily focused on long-term investment, fundamental analysis can offer valuable insights for short-term trading. Analyzing a company’s earnings reports, news announcements, and upcoming events can reveal catalysts that might trigger short-term price fluctuations. For example, a positive earnings surprise could lead to a short-term price surge, creating a day trading opportunity. Conversely, negative news or disappointing earnings could cause a temporary price drop, offering a potential short-selling opportunity.
It’s crucial to note that the impact of fundamental news on a stock’s price can vary greatly depending on the market’s overall sentiment and the specific company’s profile. Rapidly assessing the market’s reaction to fundamental news is key for successful day trading.
Charting Techniques for Identifying Entry and Exit Points
Various charting techniques aid in identifying optimal entry and exit points. Candlestick charts, for example, visually represent price movements over a specific period, offering insights into buying and selling pressure. A bullish engulfing pattern, where a large green candlestick completely engulfs a preceding red candlestick, suggests a potential price reversal to the upside. Conversely, a bearish engulfing pattern signals a potential reversal downwards.
Support and resistance levels, identified through horizontal lines drawn on price charts, represent price areas where buying or selling pressure is expected to be strong. A break above resistance often suggests a continuation of the upward trend, while a break below support may indicate a continuation of the downward trend. Trendlines, drawn by connecting significant price highs or lows, help identify the overall direction of the price movement.
Traders often look for price bounces off trendlines as potential entry points.
Reliable Resources for Real-Time Stock Market Data
Access to reliable real-time data is paramount for successful day trading. Several reputable sources provide this information. Major financial news websites, such as Yahoo Finance, Google Finance, and Bloomberg, offer real-time quotes, charts, and news updates. Dedicated financial data providers, like Refinitiv and FactSet, offer more comprehensive data sets, including advanced charting tools and analytical features, often at a subscription cost.
Brokerage platforms typically provide real-time quotes and charting tools as part of their services. It’s crucial to choose a data provider that aligns with your trading needs and budget, ensuring the data’s accuracy and reliability. Comparing data across multiple sources can help identify potential discrepancies and improve the accuracy of your analysis.
Developing a Day Trading Strategy

Crafting a successful day trading strategy requires a meticulous approach, combining market understanding with personal risk tolerance and trading style. It’s not a “one-size-fits-all” solution; your strategy should be tailored to your specific circumstances and continuously refined based on experience and market changes. This process involves several key steps.
Step-by-Step Strategy Development
Developing a robust day trading strategy involves a systematic process. First, define your trading style (scalping, swing trading, or momentum trading), which dictates your holding period and risk profile. Next, select specific markets to trade, focusing on those you understand best. Thorough market research is crucial, encompassing fundamental and technical analysis. Then, identify key indicators or patterns that signal potential entry and exit points.
Backtesting your strategy on historical data is essential to evaluate its effectiveness and refine your parameters. Finally, consistently monitor and adjust your strategy based on performance and market conditions. Remember, adaptability is key in day trading.
Risk Management Techniques in Day Trading
Effective risk management is paramount in day trading, where rapid price fluctuations can lead to significant losses. Employing a position sizing strategy, limiting the risk per trade to a small percentage of your total capital (e.g., 1-2%), is crucial. Stop-loss orders should be implemented to automatically exit a trade when a predetermined loss threshold is reached. Diversification across different assets can help mitigate risk, as can taking regular breaks to avoid emotional decision-making.
Careful monitoring of your trading performance, including win rate and average win/loss ratios, is essential for ongoing risk assessment and strategy adjustments. Never trade with money you cannot afford to lose.
Application of Different Order Types
Different order types serve specific purposes in day trading. A market order executes immediately at the best available price, suitable for quick entries or exits. A limit order specifies a price at which you are willing to buy or sell, providing more control but potentially delaying or preventing execution if the price doesn’t reach your limit. A stop-loss order automatically triggers a market order when the price falls below (for long positions) or rises above (for short positions) a predetermined level, limiting potential losses.Consider this scenario: A trader anticipates a price increase in Stock XYZ.
They place a limit order to buy 100 shares at $50. If the price reaches $50, the order executes. Simultaneously, they place a stop-loss order at $48 to limit potential losses if the price reverses. If the price drops to $48, the stop-loss order triggers a market order to sell the 100 shares, minimizing the loss. If the price rises to $52, the trader might choose to place a limit order to sell at $52 to secure profits.
Examples of Successful Day Trading Strategies
One successful strategy is mean reversion trading, which involves identifying stocks that have deviated significantly from their average price and betting they will return to the mean. This strategy requires careful analysis of price charts and the use of indicators like moving averages to identify potential reversal points. Another approach is momentum trading, which capitalizes on short-term price trends.
Traders look for stocks with strong upward or downward momentum, aiming to ride the trend for short-term profits. However, momentum can reverse quickly, necessitating tight stop-loss orders. Both strategies require rigorous analysis and disciplined risk management. For example, a successful mean reversion trader might identify a stock that has dropped sharply due to temporary negative news. They would buy at a discounted price, expecting the price to recover as the market re-evaluates the stock’s value.
A momentum trader, conversely, might focus on stocks exhibiting strong volume and price increases, aiming to profit from the continuing upward trend. These are just two examples; many other successful strategies exist, each demanding specific skills and knowledge.
Stock Market, Options, and Trading Overview
Understanding the distinctions between stock trading, options trading, and investing, along with the regulatory landscape of day trading, is crucial for success in the market. This section will clarify these differences and Artikel the compliance requirements. We will also examine the advantages and disadvantages of various trading platforms.
Stock Trading, Options Trading, and Investing: Key Differences
Stock trading involves buying and selling shares of a company’s stock. Investing, conversely, typically involves a longer-term holding period, aiming for capital appreciation through dividends and share price growth. Options trading introduces a layer of complexity, providing the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset (like a stock) at a specific price (the strike price) on or before a certain date (the expiration date).
This allows for leveraged trading and hedging strategies not available with direct stock ownership. For example, buying a call option allows you to profit from a price increase without owning the underlying shares directly, while buying a put option protects against a price decrease.
Options in Day Trading Strategies
Options are frequently employed in day trading due to their leverage and flexibility. A common strategy is using options spreads, where you simultaneously buy and sell options contracts with different strike prices or expiration dates to profit from small price movements. For instance, a bull call spread involves buying a call option with a lower strike price and selling a call option with a higher strike price.
This limits potential losses while still profiting from price increases within a defined range. Conversely, a bear put spread can be used to profit from price declines. Another strategy involves using options to hedge against risk in a stock position. For example, a trader holding a large number of shares might buy put options to protect against a sudden price drop.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance for Day Trading
Day trading is subject to stringent regulations designed to protect investors and maintain market integrity. In the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) are the primary regulatory bodies. These organizations oversee broker-dealers, impose rules on trading practices, and investigate market manipulation. Day traders must comply with regulations concerning margin accounts, pattern day trading rules (PDT), and reporting requirements.
The PDT rule, for example, restricts the number of day trades within a specified period for accounts with a balance below a certain threshold. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant penalties, including account restrictions or legal action.
Trading Platform Comparison
Choosing the right trading platform is vital for efficient and effective day trading. Different platforms offer various features, fees, and functionalities. The following table summarizes some key aspects:
| Platform | Advantages | Disadvantages | Fees |
|---|---|---|---|
| Platform A (Example: Interactive Brokers) | Wide range of instruments, advanced charting tools, robust order types | Steeper learning curve, potentially higher fees for some services | Variable, depending on usage |
| Platform B (Example: TD Ameritrade) | User-friendly interface, extensive educational resources, strong customer support | Fewer advanced features compared to some competitors | Generally lower than Platform A |
| Platform C (Example: Webull) | Commission-free trading, mobile-first design | Limited charting tools, fewer research resources | Commission-free (but other fees may apply) |
| Platform D (Example: Fidelity) | Strong reputation, diverse investment options beyond day trading, excellent research | Interface may not be as optimized for pure day trading | Competitive fees, potentially lower for high-volume traders |
Analyzing Market Trends and Volatility
Successfully navigating the day trading world requires a keen understanding of market dynamics. This involves recognizing and reacting to shifts in trends and volatility, which are heavily influenced by a variety of factors. Mastering this analysis is crucial for making informed trading decisions and maximizing profitability.
Analyzing market trends and volatility involves a multifaceted approach, encompassing the interpretation of economic indicators, news events, market sentiment, and volume data. Understanding how these elements interact allows day traders to anticipate potential price movements and adjust their strategies accordingly. Effective risk management is intrinsically linked to this analysis; accurately gauging volatility helps in setting appropriate stop-loss orders and position sizing.
Key Economic Indicators and Their Impact
Economic indicators provide valuable insights into the overall health of the economy and can significantly influence stock prices. These indicators often precede shifts in market trends, offering potential opportunities for profitable day trading. For example, a surprise increase in inflation (as measured by the Consumer Price Index or CPI) might trigger a sell-off in certain sectors, while a positive jobs report (as shown in the Nonfarm Payroll figures) could boost market sentiment.
Conversely, a decline in manufacturing activity (as reflected in the Purchasing Managers’ Index or PMI) may signal a potential downturn. Traders should monitor these reports closely and understand how different sectors typically react to specific indicators.
News Events and Geopolitical Factors
Unexpected news events and geopolitical developments can dramatically impact stock prices, sometimes leading to significant short-term volatility. A major geopolitical event, such as an international conflict or a sudden change in government policy, can cause widespread market uncertainty. Similarly, company-specific news, like a surprise earnings announcement or a product recall, can trigger rapid price fluctuations. Day traders must stay informed about current events and be prepared to adjust their strategies based on breaking news.
For instance, a sudden escalation of a trade war could negatively impact stocks in export-oriented industries, while a positive regulatory change might boost the shares of a specific company.
Interpreting Market Sentiment and Volume Data
Market sentiment reflects the overall feeling of investors towards the market. This sentiment can be gauged through various channels, including news articles, social media, and analyst reports. Positive sentiment often leads to higher prices, while negative sentiment can drive prices down. Volume data, which represents the number of shares traded, provides additional context. High volume often accompanies significant price movements, suggesting strong conviction behind those moves.
Low volume, conversely, might indicate a lack of conviction and potentially weaker price trends. For example, a significant increase in trading volume alongside a price surge indicates strong buying pressure, suggesting a potential upward trend continuation.
Incorporating Market Volatility into a Day Trading Strategy
Volatility, representing the rate and extent of price fluctuations, is a critical factor in day trading. High volatility presents both opportunities and risks. A well-defined strategy should incorporate methods to manage volatility risk. This can involve setting appropriate stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, diversifying across different stocks to reduce exposure to any single asset’s volatility, and adjusting position sizing based on the expected volatility level.
For instance, during periods of heightened geopolitical uncertainty, a trader might choose to reduce their position size or focus on less volatile stocks to mitigate potential losses. Conversely, during periods of higher volatility, options trading might offer attractive opportunities, allowing traders to leverage the price fluctuations.
Mastering the art of day trading demands discipline, a well-defined strategy, and a thorough understanding of market forces. While the potential for significant returns exists, it’s crucial to acknowledge and mitigate the inherent risks. By combining technical analysis, fundamental research, effective risk management, and emotional control, you can increase your chances of success in this competitive field. Remember that consistent learning and adaptation are key to long-term profitability in day trading.
This guide serves as a starting point on your journey; continuous refinement and practice will be crucial to your success.
Q&A
What is the minimum account balance needed for day trading?
There’s no universal minimum, but brokers often have requirements (e.g., $25,000 for Pattern Day Trading). Check with your broker.
How many trades can I make per day?
The number of trades depends on your strategy and risk tolerance. There’s no limit, but excessive trading can increase risk.
What are some common day trading mistakes to avoid?
Overtrading, ignoring stop-loss orders, emotional decision-making, and lacking a well-defined plan are frequent pitfalls.
Are there any tax implications for day trading?
Yes, day trading profits are taxed as ordinary income, so consult a tax professional for guidance.