Navigating the world of options trading can feel like charting uncharted waters, but the right platform can transform the experience. This guide delves into the diverse landscape of options trading platforms, exploring their features, costs, security measures, and educational resources. We’ll equip you with the knowledge to choose a platform that aligns perfectly with your trading style and goals, ultimately empowering you to make informed decisions in this dynamic market.
From comparing user interfaces and charting tools to understanding fee structures and risk management techniques, we’ll cover all the essential aspects. We’ll also examine the crucial relationship between stock markets, stock options, and successful trading strategies, providing a holistic understanding of this exciting and potentially lucrative field.
Introduction to Options Trading Platforms
Navigating the world of options trading requires a robust and reliable platform. The right platform can significantly impact your trading experience, from ease of execution to access to advanced tools and data. Choosing the best platform depends heavily on your individual trading style, experience level, and specific needs.Options trading platforms vary significantly in their features and functionalities. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision.
The market offers a range of platforms catering to both novice and experienced traders, each with its unique strengths and weaknesses.
Types of Options Trading Platforms
The options trading landscape includes several platform types, each designed to serve different user needs and preferences. These include web-based platforms, desktop applications, and mobile apps. Web-based platforms offer accessibility from any device with an internet connection, while desktop applications often provide more advanced charting and analytical tools. Mobile apps prioritize convenience and portability, allowing traders to manage their positions on the go.
Some platforms even integrate all three approaches, providing a comprehensive trading experience across various devices.
Key Features of Options Trading Platforms
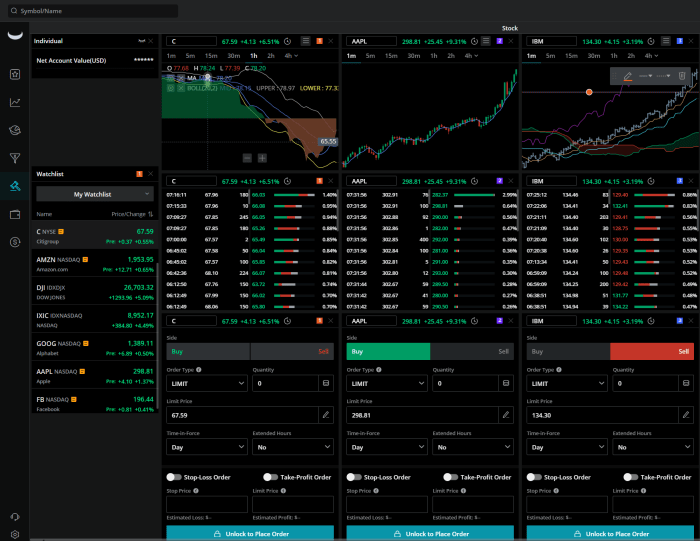
Several key features differentiate effective options trading platforms. Ease of use is paramount, especially for beginners. A user-friendly interface with intuitive navigation is essential for a smooth trading experience. Robust charting tools are vital for technical analysis, allowing traders to visualize price movements and identify potential trading opportunities. Real-time data feeds are crucial for making informed decisions, providing up-to-the-minute market information.
Advanced order types, such as limit orders, stop-loss orders, and trailing stops, offer greater control over risk management. Finally, comprehensive educational resources can significantly aid both novice and experienced traders in refining their strategies.
Examples of Popular Options Trading Platforms
Several popular platforms stand out for their unique strengths. Thinkorswim, offered by TD Ameritrade, is known for its advanced charting capabilities and extensive educational resources. Its powerful analytical tools and customizable interface cater to both beginners and experienced traders. TradeStation, another prominent platform, is renowned for its speed and reliability, particularly beneficial for active traders executing numerous trades daily.
Its robust order routing and advanced charting features make it a favorite among professionals. Finally, platforms like Interactive Brokers offer a wide range of instruments and markets, including options, futures, and stocks, making them attractive for diversified traders. The platform’s comprehensive tools and low commissions are major selling points.
Security and Reliability of Options Trading Platforms
Choosing a reliable options trading platform is crucial for protecting your investments and personal information. Reputable platforms prioritize security and adhere to strict regulatory standards to ensure a safe and trustworthy trading environment. Understanding the security measures in place and the implications of regulatory compliance is paramount for any serious options trader.Security measures employed by reputable platforms encompass a multi-layered approach designed to safeguard user data and transactions.
This includes robust encryption protocols to protect sensitive information during transmission and storage, advanced firewall systems to prevent unauthorized access, and regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. Furthermore, many platforms utilize multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security, requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before accessing their accounts. This makes it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access, even if they obtain a password.
Data Protection Measures
Reputable options trading platforms employ a range of measures to protect user data. These measures include encryption of data both in transit (using protocols like HTTPS) and at rest (using strong encryption algorithms). They also implement robust access control systems, limiting access to sensitive data only to authorized personnel. Regular security assessments and penetration testing help identify and mitigate vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Furthermore, many platforms offer features such as account alerts and transaction confirmations to help users monitor their accounts for suspicious activity. The commitment to data privacy often includes adherence to relevant data protection regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) or CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), ensuring that user data is handled responsibly and in compliance with the law.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is paramount for the security and reliability of options trading platforms. Platforms operating in regulated markets are subject to stringent oversight by financial authorities, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States or the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the United Kingdom. This oversight includes regular inspections, audits, and adherence to specific rules and regulations regarding data security, customer protection, and anti-money laundering (AML) measures.
Compliance with these regulations helps to ensure that the platform operates with integrity and transparency, protecting investors from fraud and other illicit activities. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties, including fines and even the suspension or revocation of operating licenses.
Risks of Using Less Secure Platforms
Using less secure or unregulated options trading platforms carries significant risks. These platforms may lack the robust security measures employed by reputable firms, leaving user data vulnerable to theft or unauthorized access. They may also be more susceptible to fraudulent activities, such as scams and phishing attempts. Furthermore, unregulated platforms may not offer the same level of customer protection, leaving investors with limited recourse in case of disputes or losses.
The lack of regulatory oversight also increases the risk of market manipulation and other illicit activities, potentially impacting the fairness and integrity of the trading environment. For example, a platform without adequate security measures might be easily compromised, leading to the theft of user funds or the exposure of sensitive personal information. This could have serious financial and reputational consequences for the affected users.
Educational Resources and Support
Access to comprehensive educational resources and reliable customer support is crucial for options traders of all experience levels. A robust platform will provide the tools and assistance needed to navigate the complexities of options trading, fostering confidence and ultimately, improving trading outcomes. Understanding the educational materials and support channels offered is a key factor in selecting the right platform.
Many platforms recognize the need for education and provide a variety of resources to help traders learn and grow. These resources range from beginner-friendly tutorials to advanced webinars and sophisticated analytical tools. The availability and quality of these resources significantly impact a trader’s ability to make informed decisions and manage risk effectively.
Examples of Educational Resources
Different platforms offer diverse educational resources catering to various learning styles and experience levels. For instance, some platforms provide interactive tutorials that walk users through the basics of options contracts, strategies, and risk management. Others offer on-demand webinars covering specific trading topics, presented by experienced analysts or financial professionals. Advanced research tools, such as option chain analyzers and probability calculators, are also becoming increasingly common, allowing traders to assess potential profits and losses more accurately.
Some platforms even offer simulated trading environments, allowing users to practice their strategies without risking real capital.
Customer Support Comparison
The level of customer support offered by a platform is another critical factor to consider. Prompt and helpful support can be invaluable when encountering technical issues or needing clarification on trading procedures. The following table compares the customer support offered by three hypothetical platforms – Platform A, Platform B, and Platform C.
| Platform | Phone Support | Email Support | Chat Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| Platform A | 24/7 | 24/7 | 24/7 |
| Platform B | Business Hours | 24/7 | Business Hours |
| Platform C | None | Business Hours | Business Hours |
Impact of Educational Resources on Trader Success
Access to high-quality educational resources directly correlates with a trader’s success. Traders who utilize these resources are better equipped to understand the intricacies of options trading, develop effective strategies, and manage risk appropriately. For example, a trader who completes an interactive tutorial on covered call writing will be better prepared to execute this strategy confidently and understand its associated risks and potential rewards compared to a trader with no such training.
Similarly, access to advanced research tools allows for more sophisticated analysis, potentially leading to better trade selection and improved profitability. The ability to contact customer support promptly when encountering problems ensures smoother trading operations and reduces the potential for costly errors.
Stock Market, Stock Options, and Stock Trading Relationship
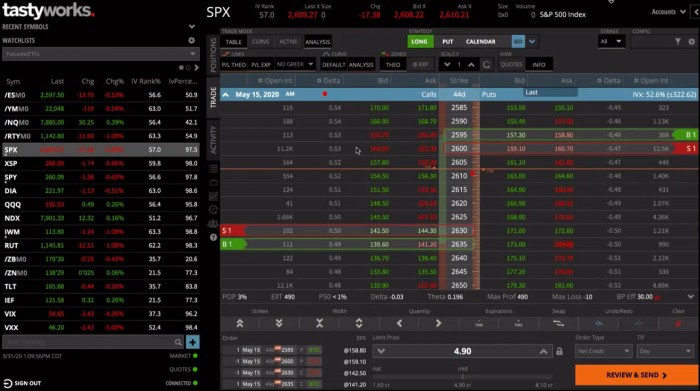
The stock market, stock options, and stock trading are intrinsically linked, forming a complex ecosystem of financial activity. Understanding their relationship is crucial for anyone participating in the market, whether as a buyer, seller, or investor. Stock options provide a powerful tool to enhance trading strategies within the broader context of the stock market.Stock options derive their value from the underlying stock traded on the stock market.
The stock market provides the platform for buying and selling shares of publicly listed companies. Stock trading encompasses the buying and selling of these shares, aiming to profit from price fluctuations. Options trading, a specialized form of stock trading, uses contracts that grant the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the underlying stock at a predetermined price (the strike price) on or before a specific date (the expiration date).
This introduces a layer of leverage and risk management not directly present in simple stock trading.
Stock Options as Trading Strategies
Stock options offer diverse strategies for managing risk and potentially enhancing returns within the stock market. They allow traders to profit from both upward and downward movements in the price of the underlying asset, unlike simple long or short positions in the stock itself. This flexibility allows for sophisticated strategies tailored to specific market outlooks and risk tolerances.
Options contracts can be used to hedge existing stock positions, speculate on price movements, or generate income through premium collection.
Examples of Stock Trading Strategies Incorporating Stock Options
Several well-established strategies utilize options to achieve specific investment goals. For example, a covered call involves selling call options on shares a trader already owns. This generates immediate income from the option premium, but limits potential upside gains if the stock price rises significantly above the strike price. Conversely, a protective put involves buying put options to safeguard against potential losses on a long stock position.
This strategy allows the trader to limit downside risk while still participating in potential upside gains. Another strategy, a straddle, involves simultaneously buying a call and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date. This strategy profits if the stock price moves significantly in either direction, but loses money if the price remains relatively stable.
Finally, a spread involves buying and selling multiple options contracts to profit from a specific price movement or range. The various types of spreads (e.g., bull call spread, bear put spread, iron condor) offer nuanced risk/reward profiles.
Risk Management in Options Trading

Options trading, while offering significant potential for profit, carries substantial risk. Effective risk management is not merely advisable; it’s absolutely crucial for long-term success and the preservation of capital. A robust strategy incorporates a variety of techniques designed to limit potential losses and maximize the chances of achieving your trading goals.
Understanding Option Greeks and Their Impact on Risk
The “Option Greeks” – Delta, Gamma, Theta, and Vega – are crucial metrics that quantify the sensitivity of an option’s price to changes in underlying factors. Understanding these Greeks is fundamental to anticipating and managing risk effectively. Ignoring them can lead to unexpected and potentially devastating losses.
Delta
Delta measures the rate of change of an option’s price for every $1 change in the price of the underlying asset. A delta of 0.50 means that for every $1 increase in the underlying asset’s price, the option’s price is expected to increase by $0.50. High delta options are more sensitive to price movements in the underlying asset, implying higher risk and reward.
Conversely, low delta options exhibit less sensitivity. For example, a deep in-the-money call option will have a delta close to 1, while a deep out-of-the-money call option will have a delta close to 0.
Gamma
Gamma measures the rate of change of an option’s delta. It indicates how quickly the delta changes as the underlying asset’s price fluctuates. High gamma options experience rapid delta changes, increasing risk as price volatility increases. For example, an option with a high gamma near the strike price will see its delta change significantly as the underlying price moves closer to or further away from the strike price.
This can lead to rapid gains or losses.
Theta
Theta represents the rate of decline in an option’s price due to the passage of time. All options lose value as they approach their expiration date, a phenomenon known as time decay. Theta is particularly significant for options with short durations to expiration. Understanding theta helps traders manage their positions before time decay erodes their potential profits.
A trader holding a long option position might consider closing the position before theta significantly impacts the value.
Vega
Vega measures the sensitivity of an option’s price to changes in the implied volatility of the underlying asset. Higher implied volatility generally leads to higher option prices. Therefore, understanding vega is crucial for managing risk in volatile markets. For example, during periods of heightened market uncertainty, vega can significantly impact option prices, leading to substantial gains or losses.
Risk Management Techniques
Several techniques can be employed to mitigate risk in options trading. These strategies are not mutually exclusive and can be combined for a more comprehensive risk management plan.
Diversification
Diversifying your options portfolio across different underlying assets and option strategies reduces the impact of losses on any single position. Instead of concentrating on a few high-risk trades, spread your investments across a range of assets and strategies to balance potential gains and losses. For example, you might hold long and short options positions on different stocks or indices.
Position Sizing
Carefully determining the size of your positions is critical. Never risk more capital than you can afford to lose on any single trade. A common rule of thumb is to risk no more than 1-2% of your trading capital on any given trade. This limits the potential damage from a losing trade and prevents significant losses from wiping out your account.
Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders automatically sell an option position when the price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses. While stop-loss orders don’t guarantee you’ll avoid losses entirely, they can help minimize the damage if the market moves against your position. Setting appropriate stop-loss levels requires careful consideration of the option’s characteristics and market conditions.
Hedging Strategies
Hedging involves taking a position that offsets the risk of another position. For example, a trader holding a long call option might hedge their position by simultaneously buying a protective put option. This reduces the potential for losses if the underlying asset’s price falls below a certain level. However, hedging strategies also reduce potential profits.
Example using a Hypothetical Platform
Let’s imagine a platform called “OptionTradr.” A trader on OptionTradr buys 10 call contracts of XYZ stock with a strike price of $100 and an expiration date of one month. The delta is 0.5. If XYZ’s price increases by $10, the trader can expect a profit of approximately $500 (10 contracts
- 100 shares/contract
- $0.5 delta
- $10 increase). However, the trader might use OptionTradr’s tools to set a stop-loss order at a price that limits potential losses to a pre-defined percentage of their capital. They might also monitor the gamma and theta to understand how the delta and time decay are affecting their position, adjusting their strategy accordingly. The platform’s charting tools and real-time data would allow them to make informed decisions based on market movements and their risk tolerance.
Choosing the Right Options Trading Platform
Selecting the optimal options trading platform is crucial for success. The right platform will streamline your workflow, offer the tools you need, and ultimately contribute to a more efficient and potentially profitable trading experience. The ideal choice depends heavily on your individual trading style, experience level, and specific needs.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Selecting an Options Trading Platform
Choosing the right platform involves careful consideration of several key factors. This step-by-step guide will help you navigate the selection process effectively.
- Define Your Trading Style and Needs: Before exploring platforms, understand your trading preferences. Are you a day trader, swing trader, or long-term investor? Do you primarily focus on specific options strategies, like covered calls or spreads? Knowing this helps narrow your search. For example, a day trader will prioritize speed and advanced charting tools, while a long-term investor might favor a platform with robust research capabilities and lower fees.
- Research and Compare Platforms: Once you’ve identified your needs, research different platforms. Consider factors like trading fees, commissions, available options contracts, charting tools, research resources, educational materials, and customer support. Many platforms offer free demo accounts, allowing you to test the interface and features before committing.
- Assess Platform Features: Evaluate features essential for your trading style. This might include advanced charting tools with technical indicators, real-time market data, option chain analysis tools, order types (limit, stop-loss, etc.), and customizable watchlists. Some platforms offer integrated news feeds and research reports, which can be valuable for informed decision-making.
- Consider User Interface and Experience: The platform’s user interface should be intuitive and easy to navigate. A cluttered or confusing interface can hinder your trading efficiency. Look for platforms with a clean layout, customizable dashboards, and easy-to-use order entry systems.
- Evaluate Security and Reliability: Security is paramount. Choose a platform with robust security measures, including encryption, two-factor authentication, and a strong track record of protecting user data. Check reviews and ensure the platform is regulated and adheres to industry best practices.
- Check Customer Support and Educational Resources: Reliable customer support is crucial, especially for beginners. Look for platforms with multiple support channels (phone, email, chat) and readily available educational resources, such as tutorials, webinars, and FAQs. A responsive and helpful support team can be invaluable when you encounter problems.
- Test the Platform with a Demo Account (if available): Most reputable platforms offer demo accounts. This allows you to practice trading without risking real money, familiarizing yourself with the platform’s features and interface before committing. This is particularly important for beginners.
- Read Reviews and Compare Pricing: Thoroughly research reviews from other users to gauge their experiences with the platform. Compare pricing structures, including commissions, fees, and data subscription costs. Different platforms have varying fee structures, so choosing one that aligns with your budget and trading frequency is important.
Illustrative Examples of Trader Needs and Platform Selection
Let’s consider two hypothetical traders with different needs and experience levels:
Trader A: Experienced Day Trader
Trader A is an experienced day trader who executes numerous trades daily. Speed, advanced charting tools, and real-time market data are paramount. They require a platform with low commissions, a robust order routing system, and customizable dashboards for efficient trade execution. A platform like “TradePro” (hypothetical) which offers ultra-low latency, advanced charting with multiple indicators, and a wide array of order types would be suitable.
The intuitive interface and advanced tools compensate for potentially higher monthly fees.
Trader B: Beginner Swing Trader
Trader B is a beginner swing trader who executes fewer trades and prioritizes ease of use and educational resources. They need a platform with a user-friendly interface, comprehensive educational materials, and strong customer support. A platform like “OptionEasy” (hypothetical) that offers a simplified interface, integrated tutorials, and excellent customer service would be more appropriate. The platform’s lower cost and focus on education would help Trader B learn and grow comfortably.
Selecting the optimal options trading platform is a pivotal decision for any trader. By carefully considering the factors discussed – platform features, cost structures, security protocols, and available educational resources – you can significantly enhance your trading journey. Remember, the right platform empowers informed decisions, effective risk management, and ultimately, greater success in the options market. Your path to confident and profitable options trading begins with informed selection.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the difference between a brokerage account and an options trading platform?
A brokerage account is a general account for holding and trading various financial instruments. An options trading platform is specialized software or a website provided by a brokerage (or sometimes independently) that facilitates options trading specifically, often with advanced charting and analysis tools.
Are there free options trading platforms?
While some platforms offer free access to basic features, most charge commissions or fees per trade, or offer tiered pricing based on account size or features used. “Free” platforms often have limitations compared to paid versions.
How do I choose a platform that suits my trading style?
Consider your experience level, trading frequency, preferred charting tools, and the types of options strategies you employ. Beginners might benefit from platforms with robust educational resources and simple interfaces, while experienced traders may prioritize advanced charting and order types.
What are the risks involved in options trading?
Options trading carries significant risk of substantial financial loss. Options contracts have expiration dates, and their value can decline rapidly. Thorough understanding of options strategies and risk management is crucial before engaging in options trading.