Navigating the world of finance can feel daunting, but understanding options trading doesn’t have to be. This guide demystifies the complexities of options, offering a clear and accessible pathway for beginners. We’ll explore the fundamental concepts, strategies, and risk management techniques necessary to confidently enter this exciting yet potentially lucrative market. From understanding calls and puts to mastering risk assessment, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
We’ll delve into real-world examples, showcasing both successful and unsuccessful trades, highlighting the crucial factors that determine outcomes. This practical approach will allow you to learn from both triumphs and setbacks, building a solid foundation for your options trading journey. We’ll also provide you with resources and tools to aid your learning and trading endeavors.
Introduction to Options Trading
Options trading offers a powerful way to participate in the market, allowing investors to profit from price movements without directly owning the underlying asset. It involves buying or selling contracts that grant the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a specific price (the strike price) on or before a specific date (the expiration date).
Understanding the fundamentals is crucial before venturing into this complex area of finance.Options trading presents both significant opportunities and substantial risks. A well-planned strategy can generate substantial profits, while a poorly executed one can lead to significant losses. This introduction will equip beginners with the basic knowledge to understand the mechanics of options trading.
Calls and Puts
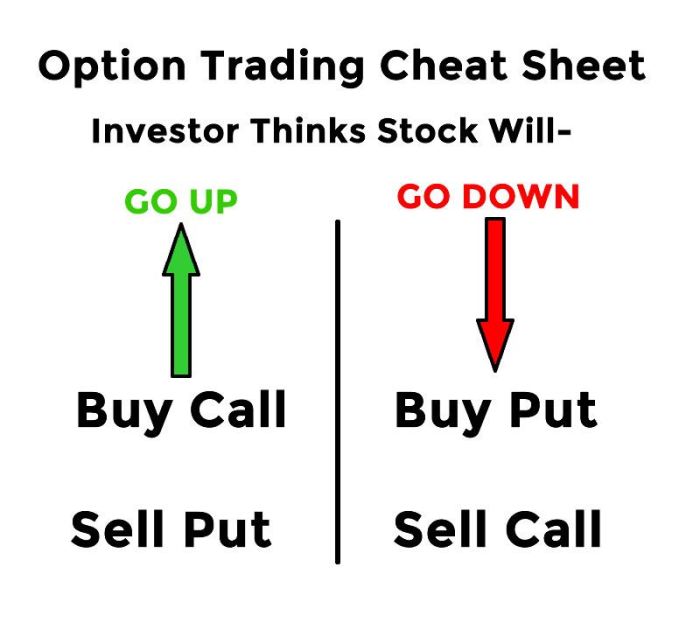
A call option gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to
- buy* an underlying asset at a predetermined price (the strike price) before or on a specific date (the expiration date). A put option, conversely, grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to
- sell* an underlying asset at a predetermined strike price before or on the expiration date.
The payoff diagram for a call option shows a profit only if the price of the underlying asset rises above the strike price plus the premium paid. The profit increases linearly with the price increase above this break-even point. Conversely, the maximum loss for a call buyer is limited to the premium paid. The payoff diagram for a put option shows a profit only if the price of the underlying asset falls below the strike price minus the premium paid.
The profit increases linearly with the price decrease below this break-even point. The maximum loss for a put buyer is also limited to the premium paid. Visualizing these diagrams is key to understanding potential profit and loss scenarios.
Successful Options Trade Example
Imagine an investor believes the price of XYZ Company stock, currently trading at $100, will rise to $115 within the next month. They purchase a call option with a strike price of $105 and an expiration date one month in the future for a premium of $2 per share. If the stock price reaches $115 at expiration, the investor can exercise the option, buying the stock at $105 and immediately selling it at $115, realizing a profit of $8 per share, less the $2 premium, resulting in a net profit of $6 per share.
Unsuccessful Options Trade Example
Consider another investor who believes the price of ABC Company stock, trading at $50, will fall below $40 within the next month. They purchase a put option with a strike price of $45 and an expiration date one month in the future for a premium of $3 per share. However, the stock price remains above $45 throughout the month. The option expires worthless, and the investor loses the entire $3 premium paid per share.
This illustrates the risk of options trading – the potential for significant losses if the market moves against the investor’s prediction.
Understanding Stock Market Basics
Before diving into the intricacies of options trading, it’s crucial to grasp fundamental stock market concepts. Understanding how stock prices behave is key to predicting and managing the risks associated with options contracts. This section will explore the relationship between stock and options prices, the factors influencing market volatility, and the characteristics of different options types.
Stock Prices and Options Prices
The price of a stock and the price of an option on that stock are intrinsically linked. Options derive their value from the underlying stock. As the stock price fluctuates, so too does the price of the options written on it. For call options (giving the buyer the right tobuy* the underlying stock at a specified price), a rising stock price increases the option’s value, while a falling stock price decreases it.
The opposite is true for put options (giving the buyer the right to
sell* the underlying stock at a specified price)
a falling stock price increases the put option’s value, and a rising stock price decreases it. This relationship is not always linear, however; factors like time to expiration and volatility play significant roles. For instance, a call option with a strike price far below the current market price will have a higher value than one with a strike price close to the market price, even if the stock price increases equally.
Factors Influencing Stock Market Volatility and its Impact on Options Pricing
Stock market volatility, measured by metrics like the VIX index, significantly impacts options pricing. Volatility refers to the rate and magnitude of price fluctuations. Higher volatility means greater uncertainty about future price movements. Several factors contribute to volatility: economic news (e.g., interest rate changes, inflation data), geopolitical events (e.g., wars, political instability), company-specific news (e.g., earnings reports, product launches), and investor sentiment (e.g., fear, greed).
Higher volatility generally leads to higher option premiums because there’s a greater chance of large price swings, increasing the potential payoff for both call and put options. Conversely, low volatility results in lower option premiums as the potential for large price movements is reduced. For example, during periods of significant economic uncertainty, like the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, we saw a surge in market volatility, leading to a sharp increase in options premiums across the board.
Types of Stock Options
The following table compares and contrasts American and European options, two primary types of stock options.
| Feature | American Options | European Options | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exercise Style | Can be exercised at any time before expiration | Can only be exercised at expiration | This impacts the option’s value and trading strategies. |
| Premium | Generally higher premium due to flexibility | Generally lower premium due to less flexibility | The premium reflects the value of the option’s features. |
| Trading Strategies | Suitable for a wider range of strategies, including early assignment | Simpler strategies, primarily focused on expiration date | The exercise style dictates suitable trading strategies. |
| Risk/Reward | Higher risk/reward profile due to early exercise potential | Lower risk/reward profile due to limited exercise timing | The timing of exercise affects the risk and potential profit. |
Stock Market, Stock Options, and Stock Trading Interrelation
The stock market, stock options, and stock trading are intrinsically linked; understanding their interconnectedness is fundamental to successful investing. Stock options derive their value directly from the underlying stock’s performance within the broader stock market. Effective options trading hinges on a robust understanding of market dynamics and stock price behavior.The stock market provides the environment in which stocks are traded and their prices determined by supply and demand.
Stock trading involves buying and selling shares of these stocks, aiming to profit from price fluctuations. Stock options, on the other hand, are derivative instruments whose value is contingent upon the price movements of the underlying stock traded in the market. Therefore, successful options trading necessitates a thorough grasp of how the stock market functions and influences stock prices.
Stock Price Movements and Options Prices
Options prices are highly sensitive to changes in the underlying stock’s price. This relationship is not linear but rather complex, influenced by factors like time to expiration, volatility, and interest rates. However, the fundamental principle remains: an increase in the underlying stock price generally benefits call options (giving the right to buy) and harms put options (giving the right to sell), while a decrease in the stock price has the opposite effect.For example, imagine a call option on Company XYZ stock with a strike price of $100 and an expiration date in three months.
If the current stock price is $95, the call option will have a low price, reflecting its low probability of being profitable at expiration. However, if the stock price rises to $110, the call option’s value will increase significantly because it is now “in the money” – the holder could exercise the option to buy the stock at $100 and immediately sell it at the market price of $110, realizing a profit.
Conversely, a put option with a $100 strike price would lose value in this scenario.
Practical Examples Illustrating Interdependence
Consider Apple (AAPL) stock. A significant news announcement about a new product launch might cause a surge in AAPL’s stock price. This immediate price increase would directly impact the value of AAPL call options, making them more valuable. Conversely, if Apple announces disappointing earnings, the stock price might plummet, decreasing the value of call options and increasing the value of put options.
These examples highlight how closely options pricing is tied to the underlying stock’s performance within the dynamic environment of the stock market. Understanding these market reactions is critical for successful options trading strategies.
The Importance of Fundamental and Technical Analysis
Successful options trading requires a combination of fundamental and technical analysis. Fundamental analysis involves assessing the intrinsic value of a company, considering factors like its financial health, competitive landscape, and future growth prospects. This helps determine whether the current stock price is undervalued or overvalued. Technical analysis, on the other hand, focuses on studying price charts and trading volume to identify trends and patterns that could predict future price movements.
Both types of analysis provide crucial information for making informed decisions about buying or selling options. For instance, identifying a strong upward trend using technical analysis might suggest buying call options, while a bearish fundamental outlook might lead to buying put options.
Educational Resources for Options Trading

Navigating the world of options trading requires a solid educational foundation. Many resources are available, ranging from free online materials to comprehensive paid courses. Choosing the right resources is crucial for building a strong understanding and minimizing risk. This section Artikels various educational avenues and offers guidance on selecting appropriate learning materials.
Reputable Educational Resources for Options Trading
Finding reliable and effective learning materials is paramount for success in options trading. The following list categorizes resources based on cost and format, offering a diverse range of options for beginners.
- Free Resources: Many websites and online platforms offer free educational content on options trading. These resources often include introductory articles, tutorials, and basic strategy explanations. Examples include Investopedia’s options trading section, which provides definitions, explanations of common strategies, and articles on risk management. The Options Industry Council (OIC) also offers free educational materials, including brochures and introductory guides designed for beginners.
While free resources can be valuable for initial learning, they often lack the depth and structured approach of paid courses.
- Paid Courses: Paid online courses provide a more structured and comprehensive learning experience. Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and Skillshare offer various options trading courses, ranging from beginner-friendly introductions to advanced strategies. These courses typically include video lectures, quizzes, and practice exercises. The cost varies depending on the platform and the course content. When choosing a paid course, consider factors such as the instructor’s experience, course reviews, and the curriculum’s comprehensiveness.
- Books: Numerous books offer detailed explanations of options trading concepts and strategies. Some popular titles include “Options as a Strategic Investment” by Lawrence G. McMillan and “The Complete Guide to Option Pricing Models” by Espen Gaarder Haug. Books often provide a more in-depth analysis than online resources and can serve as valuable references throughout your learning journey. When selecting a book, check reviews and consider the author’s expertise and the book’s relevance to your learning goals.
Key Aspects to Consider When Selecting Educational Resources
Several key factors should guide your selection of educational resources. These factors ensure that the chosen resource aligns with your learning style and goals, ultimately leading to a more effective learning experience.
- Credibility and Reputation: Prioritize resources from reputable sources with a proven track record. Look for authors or instructors with significant experience in options trading and a history of providing accurate and reliable information. Check for reviews and testimonials to gauge the quality and effectiveness of the resource.
- Curriculum and Content: The curriculum should cover fundamental concepts such as option pricing, Greeks, and various trading strategies. Ensure the content is clear, concise, and easy to understand, even for beginners. A well-structured curriculum will guide you through the learning process systematically.
- Learning Style and Goals: Consider your preferred learning style (visual, auditory, kinesthetic) when choosing a resource. If you prefer visual learning, video courses might be more suitable. If you prefer a more hands-on approach, a course with practice exercises would be beneficial. Your learning goals (e.g., basic understanding, advanced strategies) will also influence your choice of resource.
- Cost and Value: Weigh the cost of the resource against its value. While free resources are readily available, paid courses and books may offer more comprehensive and structured learning experiences. Consider the potential return on investment (ROI) in terms of increased knowledge and improved trading skills.
Options trading offers significant potential rewards, but it’s essential to approach it with a well-defined strategy and a thorough understanding of the inherent risks. By mastering the fundamentals, developing a robust risk management plan, and utilizing the available resources, you can confidently navigate the options market and potentially achieve your financial goals. Remember, consistent learning and disciplined trading are key to long-term success in this dynamic field.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the minimum account balance needed to trade options?
Minimum account balance requirements vary by brokerage. Some may allow options trading with smaller accounts, while others may require a higher minimum. Check with your broker for specifics.
How much can I lose trading options?
Potential losses can significantly exceed your initial investment, particularly with uncovered options positions. Proper risk management is crucial to mitigate potential losses.
Are options trading fees high?
Fees vary depending on the brokerage and the volume of trades. Some brokers offer commission-free options trading, while others charge per contract or have tiered fee structures. Compare fees before choosing a broker.
What are the tax implications of options trading?
Tax implications depend on your specific situation and the type of options trades you execute. Consult a tax professional for personalized advice. Capital gains taxes may apply to profits.