Navigating the world of advanced stock options strategies can feel like deciphering a complex code, but mastering these techniques unlocks potentially significant financial rewards. This guide unravels the intricacies of options trading beyond the basics, exploring sophisticated strategies like spreads and combinations, and illuminating the crucial role of understanding options Greeks. We’ll delve into real-world examples, highlighting both triumphs and pitfalls, to equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and manage risk effectively.
From understanding the underlying assets – stocks, indices, and ETFs – to mastering risk management techniques, we’ll cover the essential elements needed for successful advanced options trading. We will examine the interconnectedness of stock markets, stock options, and stock trading, showcasing how options can be strategically employed for hedging, income generation, or speculation within a broader investment portfolio.
Introduction to Advanced Stock Options Strategies
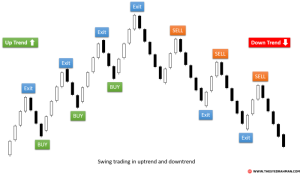
Advanced stock options strategies encompass a sophisticated set of trading techniques that go beyond the fundamental buy-and-hold or simple call/put option strategies. Their purpose is to generate potentially higher returns than basic strategies, often targeting specific market conditions or achieving precise financial goals, such as hedging against risk or profiting from market volatility. However, this increased potential for profit comes with significantly higher risk.Basic options strategies, such as buying calls or puts, primarily focus on directional bets – anticipating whether an underlying asset’s price will rise or fall.
Advanced strategies, in contrast, employ combinations of multiple options contracts (calls and/or puts) with varying strike prices and expiration dates to create complex positions designed to profit from specific market scenarios or manage risk more precisely. These scenarios might involve anticipating price movements within a specific range, exploiting volatility, or generating income regardless of the underlying asset’s price direction.
For example, a basic strategy might involve buying a call option hoping the stock price rises. An advanced strategy, like an iron condor, aims to profit from the stock price staying within a defined range.
Risk and Reward in Advanced Options Trading
Advanced options strategies inherently carry significantly higher risk than basic strategies. The complexity of these strategies introduces numerous variables that can impact the outcome, including the timing of market movements, volatility changes, and the interaction of multiple options contracts. A poorly executed advanced strategy can lead to substantial losses, potentially exceeding the initial investment. This is because the potential for losses is often amplified through the use of leverage, the purchase of multiple contracts, and the interplay of option Greeks (Delta, Gamma, Theta, Vega, Rho).
For instance, a long strangle, while potentially profitable with significant price movements, can lead to substantial losses if the underlying asset’s price remains stable.Conversely, the potential rewards from successful advanced options strategies can be considerably higher than those achievable with basic strategies. This is because these strategies often leverage market inefficiencies and volatility to generate disproportionate profits. Successful execution requires a deep understanding of option pricing models, market dynamics, and risk management techniques.
A well-executed calendar spread, for example, can generate income consistently over time while limiting risk. The key lies in careful planning, rigorous risk assessment, and a thorough understanding of the specific market conditions. However, it is crucial to remember that even the most carefully planned strategy can fail due to unpredictable market events.
Mastering advanced stock options strategies requires a blend of theoretical knowledge, practical application, and disciplined risk management. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of various sophisticated techniques, emphasizing the importance of understanding options Greeks and their impact on risk profiles. By carefully considering your market outlook, risk tolerance, and time horizon, you can leverage these strategies to potentially enhance your investment returns while mitigating potential losses.
Remember, consistent learning and practice are key to success in this dynamic field.
Questions and Answers
What is the difference between a bull call spread and a bear put spread?
A bull call spread is used when you anticipate a price increase, while a bear put spread is used when you anticipate a price decrease. They both limit potential losses but also limit potential gains compared to simply buying calls or puts.
How can I determine the appropriate position size for an advanced options strategy?
Position sizing depends on your risk tolerance and account size. A common approach is to limit the potential loss on any single trade to a small percentage (e.g., 1-2%) of your total trading capital.
What are some common mistakes to avoid in advanced options trading?
Common mistakes include overtrading, ignoring risk management principles, not understanding options Greeks, and failing to account for time decay (theta).
Are advanced options strategies suitable for all investors?
No, advanced options strategies involve significant risk and are generally not suitable for beginners. A solid understanding of options fundamentals and risk management is crucial before attempting them.