Navigating the complexities of the stock market is a constant challenge, particularly when forecasting future trends. 2024 presents a unique set of economic and geopolitical factors that will significantly shape investment strategies. This analysis delves into the key drivers expected to influence stock market performance throughout the year, providing insights into potential opportunities and risks across various sectors.
From understanding the impact of inflation and interest rate adjustments to analyzing sector-specific predictions and the role of emerging technologies, we aim to equip readers with the knowledge needed to make informed investment decisions. We’ll explore both fundamental and technical analysis techniques, emphasizing the importance of risk management and diversification in building a robust portfolio.
Stock Options Strategies for 2024

Navigating the stock market in 2024 requires a nuanced approach, and options trading offers sophisticated tools for both income generation and risk management. Understanding various strategies and their inherent risks and rewards is crucial for successful participation. This section explores several key options strategies suitable for a bullish market outlook, along with their associated risks and potential benefits.
Bullish Options Strategies
Several options strategies are well-suited for a bullish market outlook, offering potential for significant returns if the underlying asset price increases as anticipated. These strategies, however, also carry varying degrees of risk, depending on the specific approach employed. Careful consideration of these risks is vital before implementation.
Covered Call Options for Income Generation
A covered call strategy involves selling call options on shares you already own. This generates immediate income in the form of option premiums. The risk is limited to the potential loss in the underlying stock’s value if the price falls below the strike price of the sold call option. The reward is the premium received plus any appreciation in the stock price up to the strike price.For example, imagine you own 100 shares of Company XYZ trading at $50.
You could sell one covered call option contract (representing 100 shares) with a strike price of $55 and an expiration date of three months. If the stock price remains below $55 at expiration, you keep the premium received and your shares. If the stock price rises above $55, your shares will be called away at $55, resulting in a capped profit but still securing the premium.
| Strategy | Risk | Reward |
|---|---|---|
| Covered Call | Limited to stock price decline below strike price; capped upside potential. | Premium income; potential for stock appreciation up to the strike price. |
Protective Put Options for Loss Mitigation
Protective put options are a risk-management strategy used to limit potential losses on an existing stock position. This involves buying a put option with a strike price at or below the current market price of the underlying stock. The put option acts as insurance, allowing you to sell your shares at the strike price even if the market price falls significantly.For instance, if you own 100 shares of Company ABC trading at $75 and are concerned about a potential market downturn, you might buy a put option with a strike price of $70.
If the stock price falls below $70, you can exercise the put option and sell your shares at $70, limiting your loss. The cost of the put option is the premium paid, which reduces your overall profit if the stock price appreciates.
| Strategy | Risk | Reward |
|---|---|---|
| Protective Put | Premium cost; limited upside potential (premium cost offsets potential gains). | Protection against significant stock price declines; downside risk is capped at the strike price minus the premium paid. |
Stock Trading Techniques and Best Practices
Successful stock trading hinges on a blend of insightful analysis, disciplined execution, and effective risk management. This section details key techniques and best practices to navigate the complexities of the stock market and improve your trading outcomes. Understanding and applying these strategies can significantly enhance your chances of achieving your investment goals.
Fundamental Analysis for Stock Selection
Fundamental analysis involves evaluating a company’s intrinsic value by examining its financial statements, business model, competitive landscape, and overall economic environment. A thorough fundamental analysis helps determine whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued relative to its inherent worth. The process typically involves several steps:
- Company Research: Begin by researching the company’s history, products or services, management team, and competitive position within its industry. Look for companies with a strong track record of profitability, sustainable growth potential, and a solid management team.
- Financial Statement Analysis: Scrutinize the company’s balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. Key ratios to examine include price-to-earnings (P/E), price-to-book (P/B), return on equity (ROE), and debt-to-equity ratios. Compare these ratios to industry averages and historical trends to assess the company’s financial health.
- Industry Analysis: Understand the industry the company operates in. Analyze industry growth prospects, competitive dynamics, and regulatory environment. A company’s success is often intertwined with the health of its industry.
- Economic Analysis: Consider the overall macroeconomic environment. Factors such as interest rates, inflation, and economic growth can significantly impact a company’s performance.
- Valuation: After analyzing the company’s financials and industry position, determine its intrinsic value using various valuation methods such as discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis or comparable company analysis. Compare this intrinsic value to the current market price to identify potential investment opportunities.
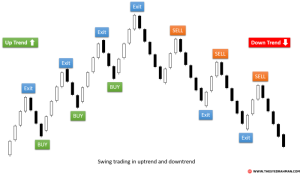
Technical Analysis for Identifying Trading Opportunities
Technical analysis focuses on interpreting historical price and volume data to predict future price movements. It utilizes charts, indicators, and patterns to identify potential entry and exit points for trades. This approach is often used in conjunction with fundamental analysis to provide a more comprehensive view of a stock’s potential.
- Chart Pattern Recognition: Identify recurring chart patterns such as head and shoulders, double tops/bottoms, and triangles. These patterns can signal potential reversals or continuations of trends.
- Technical Indicators: Utilize indicators such as moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and MACD to gauge momentum, overbought/oversold conditions, and potential trend changes. For example, a bullish crossover of a 50-day and 200-day moving average might signal a long-term buying opportunity.
- Support and Resistance Levels: Identify support and resistance levels on price charts. Support levels represent prices where buying pressure is expected to outweigh selling pressure, while resistance levels represent the opposite. Breakouts above resistance or below support can signal significant price movements.
- Volume Analysis: Analyze trading volume to confirm price movements. High volume during a price increase confirms strength, while low volume suggests weakness.
- Trend Identification: Determine the overall trend of the stock price (uptrend, downtrend, or sideways). This helps determine appropriate trading strategies, such as buying during uptrends and selling during downtrends.
Risk Management in Stock Trading
Effective risk management is crucial for long-term success in stock trading. It involves strategies to limit potential losses and protect your capital.
Implementing stop-loss orders is a fundamental aspect of risk management. A stop-loss order automatically sells a stock when it reaches a predetermined price, limiting potential losses. Position sizing, determining the appropriate amount of capital to allocate to each trade, is also essential. Diversification across multiple assets helps reduce the impact of any single investment performing poorly. Finally, thorough research and understanding your risk tolerance are paramount.
Diversification in a Stock Portfolio
Diversification involves spreading investments across various asset classes, sectors, and geographies to reduce overall portfolio risk. By diversifying, you mitigate the impact of any single investment underperforming. This approach reduces volatility and enhances the potential for consistent returns over the long term. For example, instead of investing solely in technology stocks, a diversified portfolio might include exposure to healthcare, energy, and consumer staples.
Essential Tools and Resources for Successful Stock Trading
Access to reliable information and efficient tools is vital for successful stock trading.
- Brokerage Account: A brokerage account provides access to the stock market for buying and selling stocks. Choose a reputable brokerage with competitive fees and a user-friendly platform.
- Financial News Sources: Stay informed about market trends and company news through reliable financial news websites, publications, and television channels.
- Charting Software: Technical analysis software provides charting tools, technical indicators, and other features for analyzing stock prices.
- Fundamental Data Providers: Access to financial statements, company profiles, and other fundamental data is crucial for conducting thorough research.
- Investment Tracking Software: Track your portfolio’s performance and manage your investments efficiently.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Stock Market Trading

The integration of emerging technologies is rapidly transforming the landscape of stock market trading, impacting everything from investment strategies to regulatory oversight. This evolution presents both significant opportunities and challenges for investors and market participants alike. The speed and efficiency of these technologies are fundamentally altering how markets operate and how decisions are made.
Artificial Intelligence in Algorithmic Trading
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing algorithmic trading strategies. AI-powered systems can analyze vast datasets far more quickly and efficiently than human traders, identifying patterns and making predictions with remarkable speed. Machine learning algorithms, a subset of AI, continuously learn and adapt, improving their predictive capabilities over time. This allows for the development of sophisticated trading strategies that react to market changes in milliseconds, exploiting fleeting opportunities that would be impossible for human traders to capitalize on.
For example, AI algorithms can analyze news sentiment in real-time, adjusting trading positions based on the detected emotional tone. This surpasses the capabilities of traditional rule-based systems.
Blockchain Technology and Stock Market Transparency
Blockchain technology, the underlying framework for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, offers the potential to significantly enhance the transparency and security of stock markets. Its decentralized and immutable ledger system can provide a secure and verifiable record of all transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and manipulation. By recording ownership and trades on a distributed ledger, blockchain can eliminate the need for intermediaries, streamlining the process and potentially reducing costs.
This increased transparency could lead to greater trust and participation in the market. For instance, a blockchain-based system could instantly and publicly verify the ownership of shares, eliminating the complexities and delays associated with traditional transfer processes.
Big Data Analytics and Investment Decisions
Big data analytics plays a crucial role in shaping modern investment decisions. The ability to process and analyze massive datasets—including market data, news articles, social media sentiment, and economic indicators—allows investors to identify trends and patterns that might be missed using traditional methods. Sophisticated analytical tools can uncover correlations between seemingly unrelated data points, leading to more informed investment choices.
For example, analysis of social media sentiment can provide early indicators of market shifts, allowing investors to adjust their portfolios proactively. This proactive approach, enabled by big data, offers a competitive edge in a rapidly changing market.
Challenges and Opportunities of Fintech Adoption
The increasing adoption of fintech in stock trading presents both opportunities and challenges. While fintech solutions offer increased efficiency, accessibility, and lower costs, they also raise concerns about security, regulation, and the potential for increased market volatility driven by high-frequency trading algorithms. The need for robust cybersecurity measures and clear regulatory frameworks is paramount to mitigate these risks.
However, the potential benefits of increased accessibility and lower barriers to entry for smaller investors are substantial. For instance, the rise of robo-advisors, which utilize AI-powered algorithms to manage investments, has made investing more accessible to individuals who previously lacked the resources or expertise.
Comparison of Traditional and Modern Trading Methods
| Feature | Traditional Trading Methods | Modern Technological Approaches |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Speed | Relatively slow, often manual | High-speed, automated algorithmic trading |
| Data Analysis | Limited to readily available data; manual analysis | Access to vast datasets; AI-powered analysis and prediction |
| Transaction Costs | Higher brokerage fees and commissions | Potentially lower costs due to automation and reduced intermediaries |
| Accessibility | Requires significant capital and expertise | Increased accessibility through online platforms and robo-advisors |
| Transparency | Limited transparency in some aspects of the trading process | Enhanced transparency through blockchain technology and data analytics |
Understanding Stock Market Volatility in 2024
Predicting market volatility with certainty is impossible, but understanding potential sources and developing effective risk management strategies is crucial for navigating the 2024 market landscape. This section explores key factors influencing volatility, methods for interpreting market indicators, risk management techniques, historical volatility comparisons across asset classes, and a hypothetical scenario illustrating the impact of volatility on a portfolio.
Potential Sources of Market Volatility in 2024
Several factors could significantly impact market volatility in 2024. These include persistent inflation and interest rate adjustments by central banks globally. Geopolitical instability, particularly conflicts and escalating tensions, also presents a major source of uncertainty. Furthermore, unexpected economic data releases, such as significant shifts in employment figures or inflation rates, can trigger sharp market reactions. Finally, shifts in investor sentiment, driven by news events or broader economic trends, can amplify volatility.
The interplay of these factors creates a complex environment demanding careful attention.
Interpreting Market Indicators to Gauge Volatility Levels
Several indicators help gauge market volatility. The VIX (Volatility Index), often called the “fear gauge,” measures market expectations of near-term volatility based on S&P 500 index options prices. Higher VIX values generally indicate higher expected volatility. Other indicators include the beta of individual stocks (measuring their price sensitivity relative to the overall market), historical volatility calculations (using standard deviation of past price movements), and implied volatility (derived from option prices).
Analyzing these indicators in conjunction provides a more comprehensive understanding of current and potential future market volatility.
Strategies for Managing Portfolio Risk During Periods of High Volatility
Effective risk management is paramount during volatile periods. Diversification across different asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate, etc.) reduces the impact of any single asset’s price fluctuations. Hedging strategies, such as using options or futures contracts, can help mitigate potential losses. Dollar-cost averaging (investing a fixed amount at regular intervals regardless of price) reduces the impact of market timing.
Finally, maintaining sufficient cash reserves provides flexibility to capitalize on market dips or withstand significant drawdowns. A well-defined risk tolerance level and a disciplined approach are key components of successful risk management.
Historical Volatility of Different Asset Classes
Historically, equities (stocks) have exhibited higher volatility than bonds. This is because stock prices are more sensitive to economic fluctuations and investor sentiment compared to bonds, which are generally considered safer investments. Real estate tends to have lower volatility than stocks but higher than bonds, offering a moderate risk-reward profile. Commodities like gold often act as a hedge against inflation and market uncertainty, exhibiting varying volatility depending on the specific commodity and global economic conditions.
The historical volatility of each asset class should be considered when constructing a diversified portfolio.
Hypothetical Scenario Illustrating the Impact of High Volatility
Consider a portfolio comprised of 60% equities (mostly growth stocks), 30% bonds (investment-grade corporate bonds), and 10% real estate investment trusts (REITs). A sudden geopolitical event, such as a major international conflict escalation, triggers a sharp market sell-off. The equity portion of the portfolio experiences a 20% decline, the bond portion falls by 5%, and the REITs decline by 15%.
This results in an overall portfolio loss of approximately 15%. A more conservative portfolio with a higher allocation to bonds and lower allocation to growth stocks would likely experience a smaller loss in this scenario. This highlights the importance of aligning portfolio composition with individual risk tolerance and the potential impact of unforeseen events.
The stock market in 2024 promises to be a dynamic landscape, shaped by a confluence of economic, geopolitical, and technological forces. While predicting the future with certainty is impossible, understanding the key trends and employing sound investment strategies is crucial for navigating this environment. By combining fundamental and technical analysis, diversifying portfolios, and staying informed about emerging technologies, investors can position themselves for success in the year ahead.
Remember, thorough research and risk management are paramount.
FAQ Explained
What are the biggest risks facing the stock market in 2024?
Persistent inflation, further interest rate hikes, geopolitical instability, and unexpected economic downturns are among the most significant risks.
Which sectors are expected to perform well in 2024?
While predictions vary, sectors like renewable energy, technology (specific areas within it), and potentially healthcare, depending on regulatory changes and innovation, are often cited as having growth potential. However, this is not a guarantee of success.
How can I mitigate risk in my stock portfolio?
Diversification across asset classes, employing stop-loss orders, and avoiding excessive leverage are key risk mitigation strategies.
What is the role of AI in stock market trading?
AI is increasingly used for algorithmic trading, identifying patterns, and providing insights from vast datasets. However, it’s crucial to remember that AI is a tool and doesn’t eliminate risk.